Weiwei Zhu, MS
Biography
Weiwei Zhu, MS, joined Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute's Biostatistics Unit in 2009. She works closely with Affiliate Investigator Diana Miglioretti, PhD, to design studies, manage data, and conduct statistical analyses for the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) — the National Cancer Institute’s 7-site network of mammography researchers. She has been a key member of the BCSC Statistical Coordinating Center for over 10 years. Her work studying breast screening benefits and risks played an essential role in an American Cancer Society screening guideline change in 2015.
Weiwei’s current other studies include testing the effects of sitting reduction on cardiometabolic health outcomes through a large randomized trial in older adults, studying a sedentary behavior reduction and physical activity promotion intervention for the older Latino/Hispanic community, and examining the association of the 24-hour activity cycle with cognition and physical function in older adults with Senior Investigator Dori Rosenberg, PhD, MPH. Weiwei has also collaborated on research to quantify the serious risks of misuse, abuse, and addiction associated with long-term opioid use. This multi-site study used electronic health record data and survey interviews to provide estimates of long-term opioid use risks in 2 cohorts.
After beginning her medical research career as an intern at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in 2007, Weiwei served as a biostatistician at the Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute in Florida.
Research interests and experience
-
Biostatistics
Correlated data analysis; longitudinal data; survival analysis
Medication Use & Patient Safety
Opioid misuse, abuse, and addiction
-
Cancer
Biostatistics; breast cancer screening and surveillance
Recent publications
Florez-Acevedo S, Greenwood-Hickman MA, Zhu W, Cook AJ, Delaney K, Green BB, Arterburn DE, McClure JB, Rosenberg DE Exploratory Analysis of Mental Health and Quality of Life Outcomes in a Randomized Controlled Trial to Reduce Sitting Time in Older Adults With Obesity 2025 Nov 12 doi: 10.1123/japa.2024-0387. Epub 2025-11-12. PubMed
Henderson LM, Zhu W, Onega T, Kerlikowske K, Miglioretti DL, Aiello Bowles EJ, Sprague BL, Weaver DL, Tosteson ANA, Lee CI Diagnostic management pathways for workup of abnormal screening with digital mammography versus digital breast tomosynthesis 2025 Aug;22(8):897-904. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2025.04.008. Epub 2025-04-09. PubMed
Greenwood-Hickman MA, Zhu W, Idu A, Harrington LB, McCurry SM, LaCroix AZ, Shaw PA, Rosenberg DE Associations Between 10-Year Physical Performance and Activities of Daily Living Trajectories and Physical Behaviors in Older Adults 2025 Apr 29;22(5). doi: 10.3390/ijerph22050704. Epub 2025-04-29. PubMed
Lawson MB, Zhu W, Miglioretti DL, Onega T, Henderson LM, Rauscher GH, Kerlikowske K, Sprague BL, Bowles EJA, O'Meara ES, Tosteson ANA, diFlorio-Alexander RM, Hubbard RA, Lee JM, Lee CI Disparities in Standard-of-Care, Advanced, and Same-Day Diagnostic Services among Patients with Abnormal Screening Mammography 2025 Feb;314(2):e241673. doi: 10.1148/radiol.241673. PubMed
Rosenberg DE, Zhu W, Greenwood-Hickman MA, Cook AJ, Florez Acevedo S, McClure JB, Arterburn DE, Cooper J, Owen N, Dunstan D, Perry SR, Yarborough L, Mettert KD, Green BB Sitting Time Reduction and Blood Pressure in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e243234. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3234. Epub 2024-03-04. PubMed
Research

Roundup of 3 recent studies on breast cancer screening
New research spotlights overdiagnosis, MRI before surgery, and a new way of predicting breast cancer risk
Cancer screening
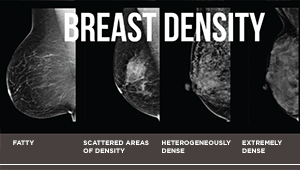
Breast density is a risk factor for older women, too
Findings in JAMA Network Open could help guide decision-making about breast cancer screening for women 75 and older.
Research

Phone therapy for insomnia shown to improve sleep
A study among KP members with sleep problems and osteoarthritis shows promise for overcoming obstacles to treatment.



